Percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen is coding as – Percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat splenic adhesions. This technique has gained increasing attention due to its effectiveness and low complication rates. In this article, we will explore the indications, technique, outcomes, and future directions of percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen.
Percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen involves the use of a flexible endoscope and laser energy to divide adhesions that have formed between the spleen and surrounding organs. This procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and can be completed in a relatively short period of time.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Adhesioloysis of the Spleen
Percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen (PEAS) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat splenic adhesions, which are bands of scar tissue that can form between the spleen and surrounding organs.
Indications for PEAS
PEAS is indicated for patients with splenic adhesions that are causing symptoms, such as:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Early satiety
- Weight loss
Technique of PEAS
PEAS is performed using a flexible endoscope that is inserted into the stomach and advanced into the splenic flexure. A laser or electrocautery probe is then used to divide the adhesions.
Outcomes of Percutaneous Endoscopic Adhesioloysis of the Spleen: Percutaneous Endoscopic Adhesioloysis Of The Spleen Is Coding As
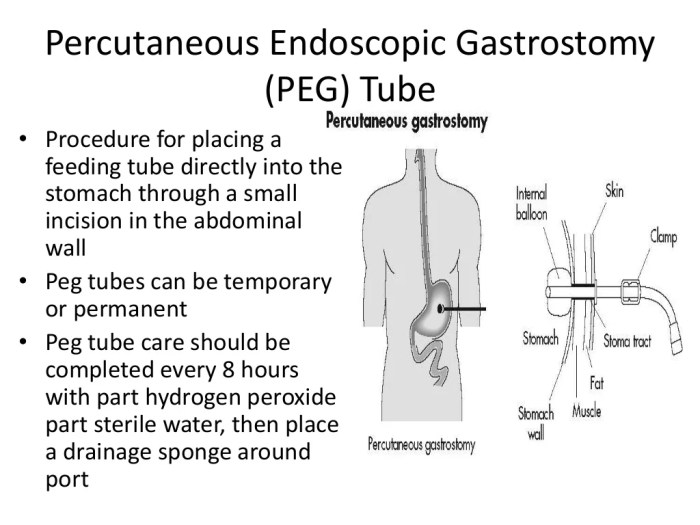
Success Rates of PEAS
The success rate of PEAS is high, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in their symptoms.
Complications of PEAS
PEAS is a relatively safe procedure, but there are some potential complications, including:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Perforation of the spleen
Comparison of PEAS to Other Treatment Options
PEAS is a less invasive alternative to open surgery for the treatment of splenic adhesions. It is also more effective than conservative management, such as pain medication and dietary changes.
Future Directions for Percutaneous Endoscopic Adhesioloysis of the Spleen

Potential Applications of PEAS in Other Clinical Settings
PEAS may be useful for treating other types of adhesions, such as those that occur after abdominal surgery or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Ongoing Research on PEAS, Percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen is coding as
There is ongoing research to improve the safety and efficacy of PEAS. This research includes studies on new laser and electrocautery probes and the development of new techniques for performing the procedure.
Challenges and Opportunities for the Future Development of PEAS
The main challenges to the future development of PEAS are the need for further research to improve the safety and efficacy of the procedure and the need for more widespread acceptance of the procedure by surgeons.
Detailed FAQs
What are the indications for percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen?
Percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen is indicated for the treatment of symptomatic splenic adhesions. These adhesions can cause pain, nausea, vomiting, and other gastrointestinal symptoms.
What are the success rates of percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen?
The success rates of percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen vary depending on the severity of the adhesions. However, studies have shown that the majority of patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms after the procedure.
What are the complications associated with percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen?
The complications associated with percutaneous endoscopic adhesioloysis of the spleen are rare but can include bleeding, infection, and damage to the spleen or surrounding organs.